Tools
The Tools page is where you configure tools that your AI Agents can use to perform actions, retrieve information, or interact with external systems. These tools are attached to Prompts and give the Large Language Model (LLM) the ability to go beyond its built-in knowledge. Tools can range from simple, pre-built functions like Google Search to complex, custom-defined functions that call your own Python code.
Prerequisites
Before you can manage Tools, ensure the following conditions are met:
- You must be logged into the application.
- Your user role must have the necessary permissions (
owner,admin,editor, ortools). - You must have an Account selected from the sidebar.
- You must have an Agent selected from the sidebar. Tools are managed on a per-agent basis.
Permissions
Access to the Tools page is controlled by user permissions. Users with owner, admin, editor, or tools permissions can manage tools.
Page Overview
The Tools page is divided into three main sections:
- Add Tool: An expandable form for creating new tool configurations.
- Tools List: A list of existing tools associated with the selected agent.
- Assign Tool: A tool to associate an existing tool (from your account) with the current agent.
Helper Buttons
- Add Variable: Opens a dialog to create a new variable that can be used within your Tools configurations
- Lookup Names: Opens a dialog to look up the exact names of Prompts, Connectors, and Variables, etc... available for the selected agent.
Creating a New Tool
To create a new tool:
- Navigate to the Tools page from the sidebar.
- Ensure an account and agent are selected.
- Expand the "New Tool" section.
-
Fill out the form with the following details:
- Tool Name: A unique, descriptive name for the tool.
- Status: A toggle to enable or disable the tool.
- Agent(s): A multi-select field to associate the tool with one or more AI Agents. Only associated agents can use this tool.
- Tool List (for pre-built tools): A text area for defining pre-built tools provided by the underlying AI model, such as
GoogleSearch(). Enter one tool per line. - Functional Declaration JSON: A text area for defining your own custom functions using an OpenAPI-compliant JSON schema. This tells the AI model what your function does, what parameters it accepts, and what it returns. This field should contain a JSON array of objects, where each object is a function declaration.
-
Click the "Create Tool" button to save the new tool.
Managing Existing Tools
Below the "Add Tool" section, all tools associated with the currently selected agent are listed.
- Each tool is displayed in its own expander, showing its name, status, and associated agents.
- Expanding a tool reveals its configuration details.
- On the right of each tool's title bar, you will find two icons:
- :material/edit: Edit: Click this to open the edit form for that tool.
- :material/delete: Delete: Click this to permanently delete the tool. A confirmation will be required.
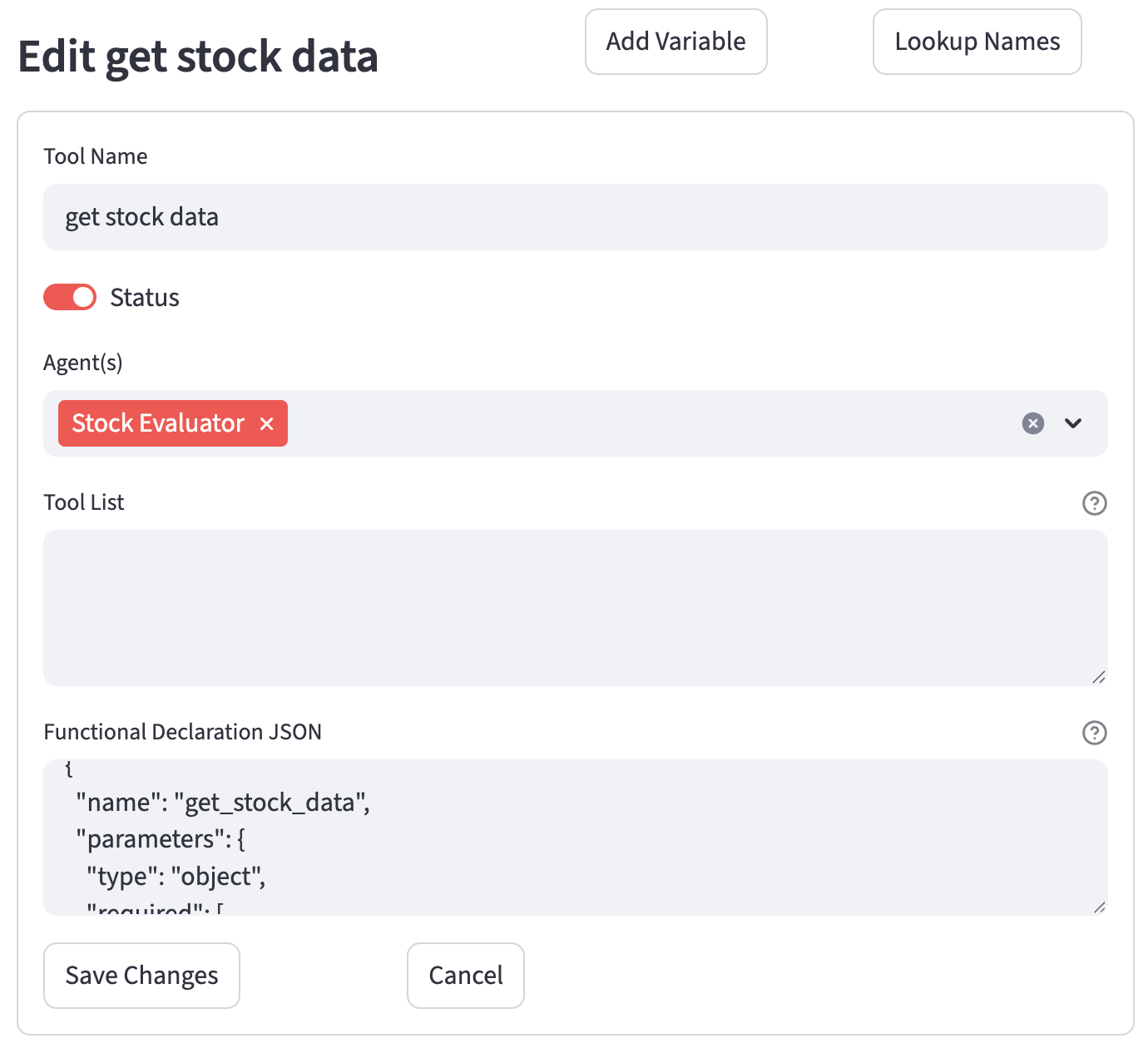
Editing an Existing Tool
- Click the "Edit" button for the tool you wish to modify.
- An edit form will appear, pre-filled with the tool's current settings.
- Click "Save Changes" to update the tool or "Cancel" to discard changes.
Deleting a Tool
Clicking the "Delete" button next to a tool will permanently remove it from the database.
Assigning a Tool to an Agent
At the bottom of the page, you may see a form titled "Assign existing Tool to '[agent_name]':".
- Select a tool from the "Available tools for [Agent Name]" dropdown.
- Click "Include Tool" to link it to the agent.
Tool Configuration and Examples
There are two primary ways to define tools for your agent.
1. Pre-built Tools
These are used for built-in functionalities provided by the AI model provider (e.g., Google). You define them in the Tool List field.
Example: Grounding with Google Search This allows the model to search Google to ground its responses in real-time information.
Example: URL Context Search This allows the model to search a specific URL for context.
Example: Code Execution This enables the model to execute code to solve computational problems.
Example: RAG with a Vertex AI Store This configures a tool for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) using a defined RAG store. You can only have one defined RAG store per agent.
Tool(retrieval = RagStore(<name of store here>))
# replace <name of store here> with the name of the desired RAG store
Functional Declaration Examples
2. Custom Functions (Functional Declarations)
You can define your own custom tools by providing a function schema in the Functional Declaration JSON field. This tells the LLM what your function does and what parameters it needs. Important: For every function you declare here, you must create a corresponding Python function with the exact same name inside the pinionai_extensions.py file. The pinionai/client.py file automatically imports these functions so they can be called by the agent.
Using Variables for Dynamic Context
A powerful feature is the ability to embed agent variables directly into your function declarations using the {var["variable_name"]} syntax. When the LLM considers using your tool, these placeholders are dynamically replaced with the current values from the agent's session. This gives the LLM crucial context about what values to use for the function's parameters.
Please note with {var['variable']}, you can easily pass values to functions in pinionai_extensions.py
Example 1: Stock Data Function
This declaration defines a tool named get_stock_data. The description fields for its parameters tell the LLM to use the values from the agent's stock_symbol and alphavantage_key variables.
{
"name": "get_stock_data",
"description": "Fetches stock data from the Alpha Vantage API. Use this to get stock prices, company overviews, and other financial data.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"stock_lookup_function": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The specific Alpha Vantage function to call. We will use the following function {var['stock_lookup_function']}"
},
"stock_symbol": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The stock ticker symbol for the company. we will use {var['stock_symbol']}"
},
"alphavantage_key": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The API key required for authenticating with the Alpha Vantage service. We will use {var['alphavantage_key']}"
},
"interval": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The time interval for time series data, e.g., '5min', '15min', '60min'. Required for functions like 'TIME_SERIES_INTRADAY'."
}
},
"required": ["stock_lookup_function", "stock_symbol", "alphavantage_key"]
}
}
Corresponding Python Function
The above JSON declaration requires the following async function to be defined in /pinionai_extensions.py. The LLM will use the arguments from the user's request to call this function.
# Stock Market Tool
async def get_stock_data(
stock_lookup_function: str | None = None,
stock_symbol: str | None = None,
alphavantage_key: str | None = None,
interval: str | None = None,
) -> dict:
"""
Fetches stock data from the Alpha Vantage API.
"""
# Filter out None values from parameters
params = {
"function": stock_lookup_function,
"symbol": stock_symbol,
"apikey": alphavantage_key,
"interval": interval,
}
params = {k: v for k, v in params.items() if v is not None}
try:
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
base_url = 'https://www.alphavantage.co/query'
response = await client.get(base_url, params=params, headers={"User-Agent": "none"})
logging.debug(f"Stock check Response URL: {response.url}")
response.raise_for_status()
# convert to markdown
stock_data = response.json()
return await format_stock_data_as_markdown(stock_data)
except httpx.HTTPStatusError as http_err:
logging.error(f"HTTP error occurred: {http_err} - {http_err.response.text}")
return {"error": f"HTTP error: {http_err.response.status_code}", "message": http_err.response.text}
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"An unexpected error occurred: {e}")
return {"error": "An unexpected error occurred.", "message": str(e)}
Pro Tip: Collecting inputs in the Intent
Remember, you need to make sure you have Intents such as check share price (information intent) and stock ticker symbol and stock research type (inputs) which will collect and set the stock_symbol and stock_lookup_functions variables.
The check share price intent should include a completed Required Variable Inputs (JSON) field like the following
{
"stock_symbol": "What is the stock ticker to you want to check",
"stock_lookup_function": "What do you want to check. You can say GLOBAL_QUOTE for current price information, TIME_SERIES_INTRADAY for today's price action, or TIME_SERIES_DAILY for recent price moves."
}
Example 2: Temperature Function This example defines a tool to get the current temperature for a location, also using variables.
{
"name": "get_current_temperature",
"description": "Gets the current temperature for {var['location']}.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The location name, e.g. San Francisco. We will use {var['location']}"
},
"units": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Units for temperature, like {var['units_of_temperature']}.",
"default": "fahrenheit"
}
},
"required": ["location"]
},
"notes": ["This is a note about {var['location']}.", "Another note."]
}