Parsers
The Parsers page in the application allows users to define and manage parsers. Parsers are used to extract data from a source variable (which might contain structured data like JSON, XML, CSV, or plain text) and map the extracted values to other variables within the system. This is useful for processing API responses, user inputs, or any other data that needs to be broken down into usable pieces.
Overview
The page provides functionalities to:
- Add new parsers.
- List existing parsers, filtered by the selected agent.
- Edit existing parsers, including their variable mapping.
- Associate parsers with specific agents.
- Delete parsers.
- View quick help examples for variable path usage.
Adding a New Parser
To add a new parser:
- Navigate to the Parsers page.
- Expand the "New Parser" section.
- A form will appear with the following fields:
- Parser Name: (Text Input) A unique and descriptive name for the parser (e.g., "ExtractUserDetails", "ProcessOrderResponse").
- Status: (Toggle) Activates or deactivates the parser. Default is
True(active). - Agent(s): (Multiselect) Select one or more agents that will be able to use this parser.
- Source Variable: (Selectbox) The variable whose content will be parsed.
- Parser Type: (Selectbox) The format of the data in the source variable. Options:
json,xml,csv,text. - Text Parse Method: (Selectbox) If
Parser Typeistext, this specifies the method. Options:regex,split,partition. - Text Delimiter: (Text Input) If
Parser TypeistextandText Parse Methodissplitorpartition, this is the delimiter character(s). Default is,. - Variable Mapping UI:
- This section allows you to define how data extracted by the parser is mapped to destination variables.
- For each mapping, you provide:
- Variable Name: (Selectbox) The destination variable where the extracted value will be stored.
- Variable Path: (Text Input) The path or expression to locate the data within the source variable. The interpretation of this path depends on the
Parser Type: json: A JSONPath expression (e.g.,$.user.name,$.items[0].id).xml: An XPath-like path (e.g.,user/name,items/item[0]/id). (Note: The current implementation might use simple dot notation for XML, see Quick Help for examples).csv: The column name from the CSV data.text:- For
regex: The regular expression. - For
split/partition: The index of the part (0-based).
- For
- Click "Add Map Variable" to add more mapping rows. Initially, four rows are shown.
- Click the "Create Parser" button.
- Upon submission, the system stores the parser configuration, including the variable mapping as a JSON object.
Listing Parsers
Existing parsers are listed under the "Parsers" subheader.
- Filtering: The list is automatically filtered to display parsers associated with the globally selected agent (if an agent is selected).
- Display: Each parser is shown in an expandable section, displaying its name, type, status (✅ for active, ❌ for inactive), and associated agents.
- Details: Expanding a parser's section reveals:
- Source Variable
- Parser Map (the JSON object defining variable mappings, collapsed by default)
- Each parser entry has "Edit" and "Delete" buttons.
Editing a Parser
To edit an existing parser:
- Click the "Edit" button next to the desired parser in the list.
- The "Edit [Parser Name]" form will appear, pre-filled with the parser's current information.
- All fields from the "Add Parser" form are available for modification.
- The "Value Mapping (JSON)" is displayed as a text area showing the raw JSON of the mapping.
- Buttons above the form:
- Edit Mapping: (Button) Opens a dialog to interactively edit the variable-to-path mappings. See "Editing Parser Mapping" below.
- Add Variable: (Button) Opens a dialog to quickly add a new variable if needed during configuration.
- Lookup Names: (Button) Opens a dialog for looking up existing system names.
- Click "Save Changes" to update the parser or "Cancel" to discard changes and hide the edit form.
Editing Parser Mapping
When you click the "Edit Mapping" button in the edit form, a dialog appears:
- The dialog displays the current mappings, similar to the "Add Parser" UI.
- You can modify existing mappings (change destination variables or paths) or add new ones.
- Click "Add Map Variable" within the dialog to add more mapping rows.
- Click "Save Mapping" to save changes to the mapping and close the dialog. The main "Edit Parser" form will reflect these changes in the "Value Mapping (JSON)" text area.
- Click "Cancel" to close the dialog without saving mapping changes.
Adding an Agent to a Parser
If an agent is selected (via the global agent selector), a section appears allowing you to associate existing parsers (that are not already associated with the selected agent) to that agent.
- A dropdown lists "Available Parsers for [Selected Agent Name] Agent:".
- Select a parser and click "Include Parser" to add the selected agent to that parser's
parser_agentslist.
Deleting a Parser
To delete a parser:
- Click the "Delete" button next to the desired parser in the list.
- Confirm the deletion when prompted. The parser will be permanently removed from the database.
Quick Help - Real World Parser Examples
JSON Parsing (using JSONPath)
This example shows how to parse a customer variable containing a JSON object returned from an API.
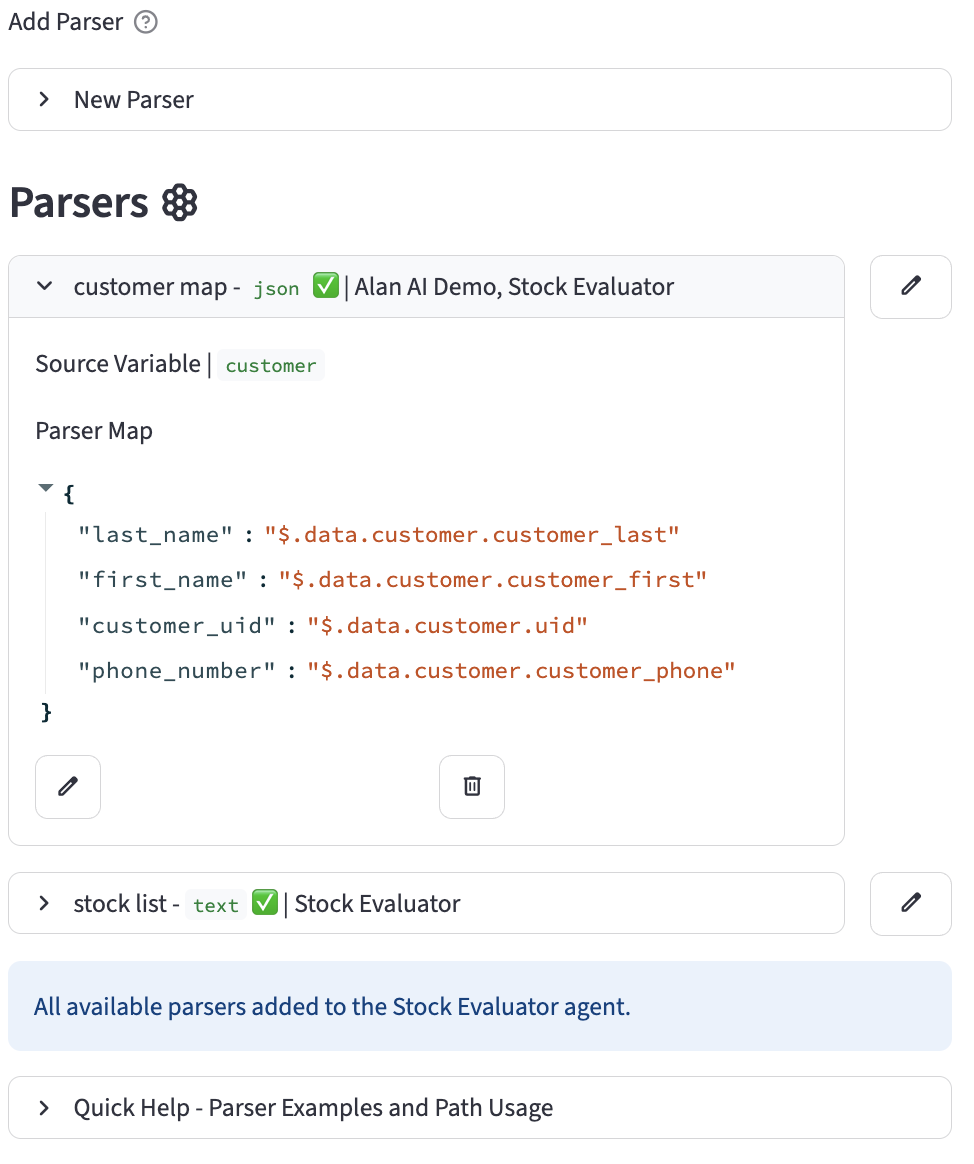
- Parser Name:
customer map - json - Source Variable:
customer
Example JSON in customer variable:
{
"data": {
"customer": {
"uid": "cust_abc123",
"customer_first": "Jane",
"customer_last": "Doe",
"customer_phone": "555-867-5309"
}
}
}
Parser Map Configuration:
{
"first_name": "$.data.customer.customer_first",
"last_name": "$.data.customer.customer_last",
"customer_uid": "$.data.customer.uid",
"phone_number": "$.data.customer.customer_phone"
}
This configuration will extract the values from the JSON and place them into the first_name, last_name, customer_uid, and phone_number variables respectively.
XML Parsing (using simple dot notation)
If your source variable contains XML, use dot notation to navigate the structure. Note: This method does not support indexing into lists of elements (e.g., orders.order[0]). To access a list, extract the parent element.
Example XML in source variable:
<root>
<customer>
<id>123</id>
<name>John Doe</name>
<orders>
<order><id>A1</id></order>
<order><id>B2</id></order>
</orders>
</customer>
</root>
Parser Map Configuration:
{
"customer_name": "root.customer.name",
"customer_id": "root.customer.id",
"order_list": "root.customer.orders"
}
CSV Parsing
If your source variable contains CSV data, the path is simply the column header. The result will be a list of all values in that column.
Example CSV in source variable:
Parser Map Configuration:
This will create a product_names variable with the list ['Laptop', 'Mouse', 'Keyboard'] and a price_list variable with [1200, 25, 75].
Text Parsing
Method: split
This example shows how to parse a stock_list variable containing a comma-separated string.
- Parser Name:
stock list - text - Source Variable:
stock_list - Text Parse Method:
split - Text Delimiter:
,
Example Text in stock_list variable: GOOG,MSFT,AAPL
Parser Map Configuration:
This configuration will create a stockA variable with the value GOOG, a stockB variable with MSFT, and a stockC variable with AAPL.
Method: regex
If the source variable is User email is test@example.com and you want to extract the email:
Parser Map Configuration:
This will create a user_email variable with the value test@example.com.
Common Regex Patterns:
• \d+ - Match one or more digits
• \w+ - Match one or more word characters
• \s+ - Match one or more whitespace characters
• [a-zA-Z] - Match any letter
• . - Match any character except a newline
• ^ - Match the start of a string
• $ - Match the end of a string
• ( ) - Capture group
This documentation should provide a good understanding of how to use the Parsers page.