Connectors
The Connectors page in the application allows users to define and manage OAuth connectors. These connectors are used to generate Bearer tokens for authenticating with external APIs, enabling secure communication between your AI agents and third-party services.
Overview
The page provides functionalities to:
- Add new connectors.
- List existing connectors, filtered by the selected agent.
- Edit existing connectors.
- Delete connectors.
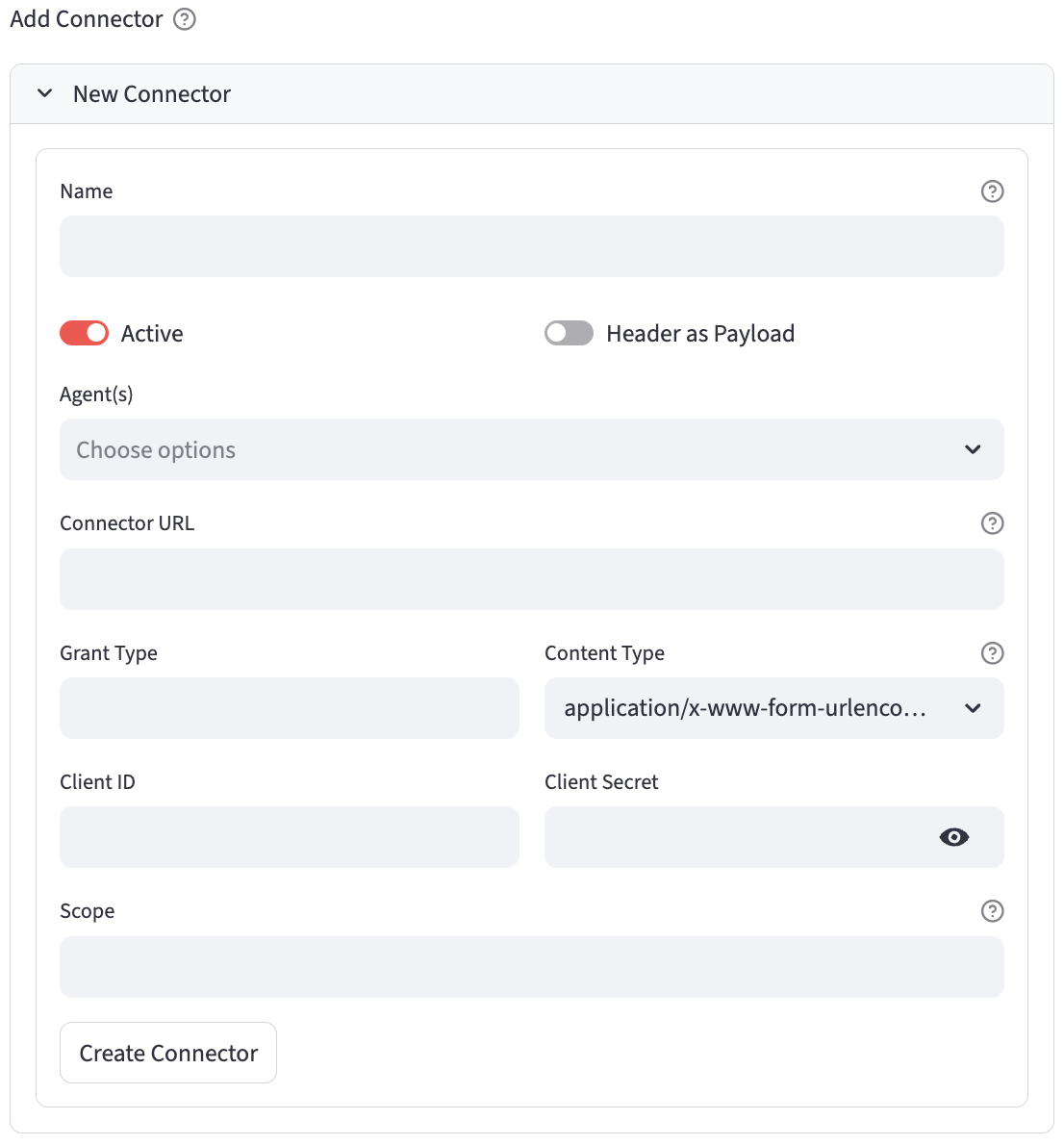
Adding a New Connector
To add a new connector:
- Navigate to the Connectors page.
- Expand the "New Connector" section.
- A form will appear with the following fields:
- Name: (Text Input) A unique and descriptive name for the connector (e.g., "MyServiceOAuth", "JourneyIDConnector"). This name acts like a variable and cannot contain spaces.
- Active: (Toggle) Activates or deactivates the connector. Default is
True(active). - Header as Payload: (Toggle) Specifies if the client ID and secret should be sent in the header (typically as a Basic Auth string) or as part of the request body payload. Default is
False(sent in payload). - Agent(s): (Multiselect) Select one or more agents that will be able to use this connector.
- Connector URL: (Text Input) The URL endpoint of the OAuth token provider (e.g.,
https://auth.example.com/oauth/token). - Grant Type: (Text Input) The OAuth grant type (e.g., "client_credentials"). This can also be a special type for cloud storage, like
gcs_service_accountoraws_iam. See the Quick Help section for details. - Content Type: (Selectbox) The content type of the token request. Options:
application/x-www-form-urlencoded,application/json. - Scope: (Text Input, Optional) The scope of the access request for OAuth 2.0. This is a space-separated list of permissions the application is requesting (e.g., "read:user write:repo").
- Client ID: (Text Input) The client ID provided by the OAuth service.
- Client Secret: (Password Input) The client secret provided by the OAuth service or json key or secret for cloud file storage.
- Service Account Email (optional): The GCP service account email to grant bucket access to when using this connector. Will be used for building RAG Stores.
- Click the "Create Connector" button.
- Upon submission, the system stores the connector configuration.
Listing Connectors
Existing connectors are listed under the "Connectors" subheader.
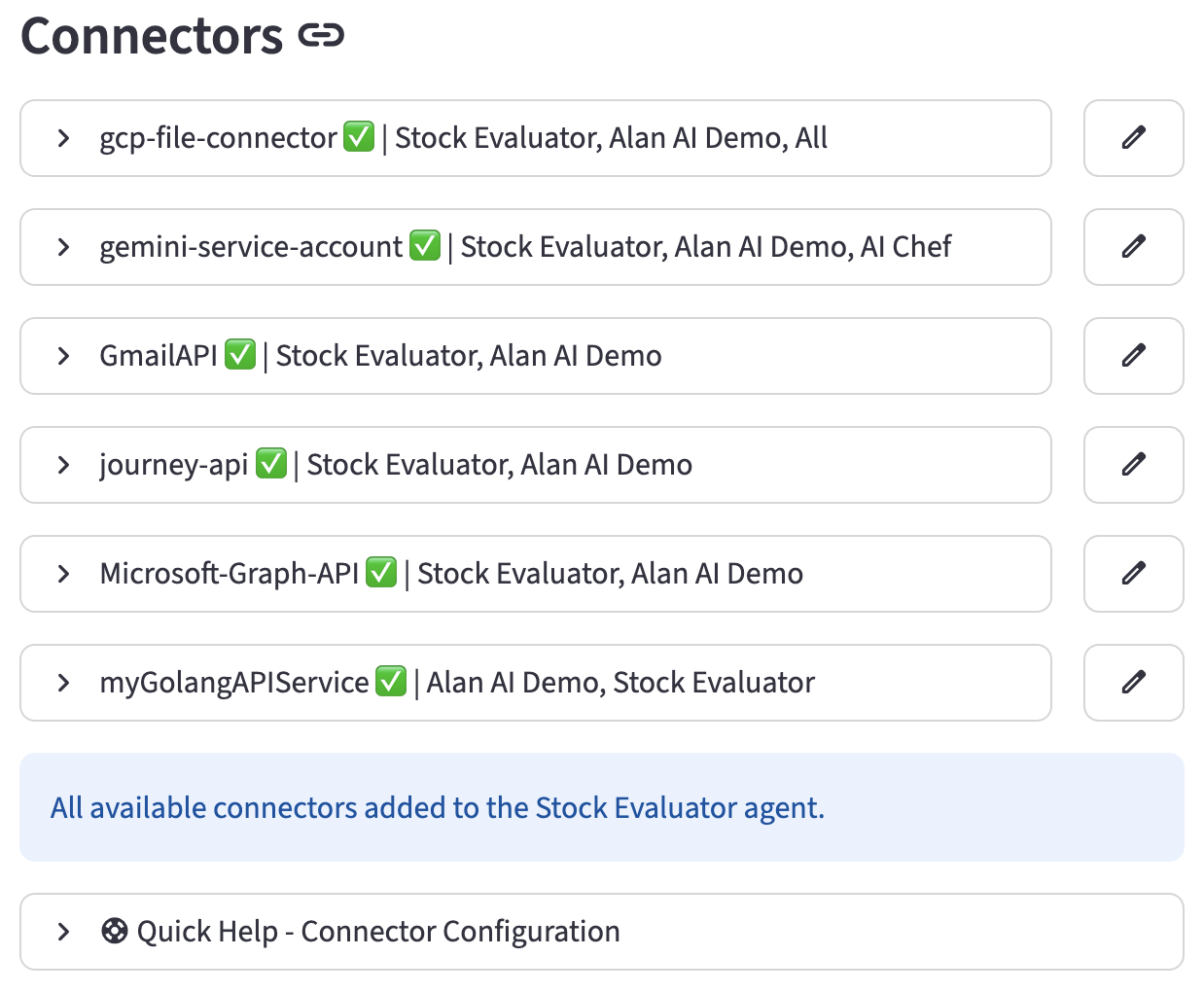
- Filtering: The list is automatically filtered to display connectors associated with the globally selected agent (if an agent is selected in the application's main navigation/sidebar).
- Display: Each connector is shown in an expandable section, displaying its name, status (✅ for active, ❌ for inactive), and associated agents.
- Details: Expanding a connector's section reveals:
- Client ID
- URL
- Grant Type
- Content Type
- Each connector entry has "Edit" and "Delete" buttons.
Editing a Connector
To edit an existing connector:
- Click the "Edit" button next to the desired connector in the list.
- The "Edit [Connector Name]" form will appear, pre-filled with the connector's current information.
- All fields from the "Add Connector" form are available for modification.
- The "Client Secret" will be displayed as a password input field.
- Click "Save Changes" to update the connector or "Cancel" to discard changes and hide the edit form.
Deleting a Connector
To delete a connector:
- Click the "Delete" button next to the desired connector in the list.
- Confirm the deletion when prompted (though the code doesn't explicitly show a confirmation dialog, it's standard practice). The connector will be permanently removed from the database.
How Connectors are Used
Connectors defined on this page can be selected when configuring items on the APIs page or the Files page.
For APIs (OAuth 2.0)
When an API call is made that uses one of these connectors for authentication:
- If "Header as Payload" is
False(default): The system makes a POST request to the "Connector URL" with "Client ID", "Client Secret", and "Grant Type" in the request body (formatted according to "Content Type") to obtain a Bearer token. - If "Header as Payload" is
True: The system makes a POST request with "Client ID" and "Client Secret" typically encoded in anAuthorization: Basic <base64_encoded_credentials>header, and "Grant Type" in the body, to obtain a Bearer token. - The obtained Bearer token is then automatically included in the
Authorizationheader of the actual API call being made by the agent.
For Files (Cloud Storage)
When a File operation uses a connector for Google Cloud Storage or AWS S3, the connector provides the necessary credentials directly, rather than fetching a token.
- GCS: The connector provides the service account key from the
Client Secretfield. - S3: The connector provides the AWS Access Key and Secret from the
Client IDandClient Secretfields.
This documentation should provide a good understanding of how to use the Connectors page.
Example Help - Connector Configuration
Connectors are used to securely store credentials and obtain authentication tokens (like OAuth Bearer tokens) for external services.
Common OAuth Grant Types
When setting up a connector for a service that uses OAuth 2.0, you'll often use one of the following Grant Type values:
client_credentials: This is a common grant type for server-to-server communication where the application is authenticating itself, not on behalf of a user. You will typically provide aClient IDandClient Secret.- Basic Auth: If the service uses Basic Authentication, you can enable the Header as Payload toggle. This will encode the
Client IDandClient Secretinto a standardAuthorization: Basic ...header.
Gemini/Vertex AI Connectors (for non-GCP hosted agents)
To allow PinionAI agents to use Gemini/Vertex AI when not hosted in GCP, you must add a service account with the appropriate permissions to the Agent configuration in Pinion AI. A service account is a special type of Google account intended to represent a non-human user (like an application) that needs to authenticate and be authorized to access data in Google APIs. Configure connectors with the following special grant types:
For Google Gemini/Vertex AI Access (non-GCP hosted):
connector_grant_type: Set this togcs_service_account.connector_client_id: Can be left blank or used for the GCP Project ID.connector_client_secret: Paste the entire JSON content of your GCP service account key file here.
Note on GCP Permissions: Ensure that the service account associated with the provided key has the necessary permissions you desire. Use Gemini/Vertex AI User (roles/aiplatform.user) for example.
Cloud Storage Connectors (for Files)
To allow agents to read and write files from cloud storage or for use in Stores building a RAG with Vertext AI, configure connectors with the following special grant types:
For Google Cloud Storage (GCS):
Grant Type: Set this togcs_service_account.Client ID: Can be left blank or used for the GCS Project ID.Client Secret: Paste the entire JSON content of your GCS service account key file here.
Note on GCP Permissions: Ensure that the service account associated with the provided key has the necessary permissions you desire. Use Storage Object Admin (roles/storage.objectAdmin) for managing files inside and existing buckets. If you want PinionAI to also create buckets, use Storage Admin (roles/storage.admin) for read/write access on the specific GCS buckets you intend to use. You can also specify a service account email in the "Service Account Email" field to grant bucket access to that specific service account when using this connector.
For AWS S3:
Grant Type: Set this toaws_iam.Client ID: Your AWS Access Key ID.Client Secret: Your AWS Secret Access Key.
Note on Default Credentials: If no connector is specified for a GCS or S3 file operation, the system will attempt to use Application Default Credentials (for GCS) or environment variables/IAM roles (for S3). This is ideal for services running directly on GCP or AWS.
Steps to Create a Google Service Account and Download Key File
- Go to the Google Cloud Console.
- Select your project or create a new one.
- Navigate to "IAM & Admin" > "Service Accounts".
- Click "Create Service Account".
- Fill in the service account details and click "Create".
- Grant the service account the necessary roles (e.g., Vertex AI User).
- Click "Done" to finish creating the service account.
- Find your service account in the list and click on it.
- Go to the "Keys" tab and click "Add Key" > "JSON".
- A JSON key file will be downloaded to your computer. This file contains the credentials needed to authenticate as the service account. Use the contents of this file in the
Client Secretfield of your connector.
Configuring Connector to be used for sending emails via the Gmail API
Here is a guide on how to generate a refresh token from Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and how to configure PinionAI to use it for sending emails via the Gmail API.
This process involves two main parts:
- Generating Credentials in GCP: Creating the necessary
Client ID,Client Secret, andRefresh Token. - Configuring Your Connector: Structuring the
Connectorto successfully obtain an access token.
Part 1: Generating a Google API Refresh Token
The easiest way to generate a long-lived refresh token is by using the Google OAuth 2.0 Playground.
Step 1: Create OAuth 2.0 Credentials in GCP
- Go to the Google Cloud Console.
- Ensure you have a project selected. If not, create one.
- In the navigation menu, go to APIs & Services > Enabled APIs & services. Click + ENABLE APIS AND SERVICES, search for "Gmail API", and enable it.
-
Go to APIs & Services > OAuth consent screen.
-
User Type: Choose External.
- App Information: Fill in an "App name" (e.g., "My Streamlit App"), your "User support email", and "Developer contact information".
- Scopes: Click Add or Remove Scopes. Find and add the .../auth/gmail.send scope.
-
Test Users: Add the Google account email address you will use to authorize the application (e.g., your own Gmail address).
-
Go to APIs & Services > Credentials.
-
Click
+ Create Credentialsand select OAuth client ID. - Application type: Select Web application.
- Name: Give it a descriptive name (e.g., "Gmail Sender Credentials").
- Authorized redirect URIs: Click + ADD URI and enter https://developers.google.com/oauthplayground. NOTE: You will need to edit this later. Google's OAuth 2.0 security requires that you explicitly list every single URL that your application is allowed to redirect to after a user grants consent. In the instructions, we are using the
Google OAuth 2.0 Playgroundto act as a temporary stand-in for your app to get the refresh token. - Click
Create. A window will pop up with your Client ID and Client Secret. Copy these two values. You will need them in the next step and for your final configuration.
Step 2: Use OAuth 2.0 Playground to Get a Refresh Token
- Open the
Google OAuth 2.0 Playground. - In the top-right corner, click the gear icon (⚙️ OAuth 2.0 Configuration).
- Check the box for Use your own OAuth credentials.
- Paste your Client ID and Client Secret into the fields.
- On the left, under "Step 1: Select & authorize APIs", find "Gmail API v1" and select the scope you authorized earlier: https://www.googleapis.com/auth/gmail.send.
- Click the Authorize APIs button. You will be prompted to sign in with the test user account you configured. Grant the requested permissions.
- You will be redirected back to the playground with an "Authorization code". Click the Exchange authorization code for tokens button.
- On the right side, you will now see your Refresh token and an initial Access token. Copy the Refresh token. This is the long-lived token your application will use.
Part 2: Configuring the Connector
Now, you can use the credentials you generated to configure your connector. Make sure the connector configuration is correct.
Here is how you should structure the Gmail connector:
- "name": "GmailAPI",
- "url": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token",
- "clientId": "YOUR_CLIENT_ID_FROM_GCP",
- "clientSecret": "YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET_FROM_GCP",
- "grantType": "refresh_token",
- "refreshToken": "THE_REFRESH_TOKEN_FROM_OAUTH_PLAYGROUND",
- "contentType": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
- "scope": "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/gmail.send"
Explanation of the fields:
- "url": This is Google's endpoint for exchanging tokens.
- "clientId": The client ID you generated in Part 1.
- "clientSecret": The client secret you generated in Part 1.
- "grantType": "refresh_token": This is critical. It tells Google that you are using a refresh token to get a new access token. Your code correctly uses this value to build the request.
- "refreshToken": The long-lived refresh token you generated in Part 1.
- "contentType": Google's token endpoint expects the data in this format. Your code correctly handles this by building a URL-encoded form data string.
- "scope": While not always required for a refresh request, it's good practice to include it.
When PinionAI calls this configuration, it will make a POST request to Google, which will return a new, short-lived access_token. This token can then be passed directly to send the email.
Troubleshooting
IF you received the Error 400: redirect_uri_mismatch because the application you configured in the Google Cloud Console does not have the correct "Authorized redirect URI" registered.
Why This Happened
This could be a timing issue, since it takes 5 minutes to a couple of hours to original set. However, Google's OAuth 2.0 security requires that you explicitly list every single URL that your application is allowed to redirect to after a user grants consent. In the instructions, we are using the Google OAuth 2.0 Playground to act as a temporary stand-in for your app to get the refresh token.
The error message indicates that the URI for the playground, https://developers.google.com/oauthplayground, was not added to the approved list for your OAuth Client ID. This is a common oversight.
How to Fix It
You need to edit your OAuth Client ID in the Google Cloud Console and add the correct redirect URI.
-
Go back to the Google Cloud Console Credentials page.
-
Find the OAuth 2.0 Client IDs section and click on the name of the client ID you created earlier (the one you named "Gmail Sender Credentials" or similar).
This will open the configuration page for that client ID. Scroll down to the Authorized redirect URIs section.
Click + ADD URI
In the new text field that appears, paste the following URL exactly as it is written:
https://developers.google.com/oauthplayground
Ensure there are no typos and that it uses https.
Scroll to the bottom and click the Save button.
After saving, wait about 5 minutes to a few hours for the change to take effect, and then try the OAuth 2.0 Playground steps again. The authorization should now proceed without the mismatch error.